Are you looking for therapy to treat your symptoms?
Discover Medical Cannabis
If you’re wondering how it works, what benefits it offers, and why more and more people are using it for their well-being, keep reading.
You’ll find all the answers about how medical cannabis can improve your quality of life.
What is Medical Cannabis?
When we talk about “Medical Cannabis“, we refer to the medical use of the cannabis plant and its active components, cannabinoids, for the treatment of specific medical conditions.
Medical Cannabis contains a large number of cannabinoids, which are the focus of extensive scientific research. The two most well-known compounds are CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol).
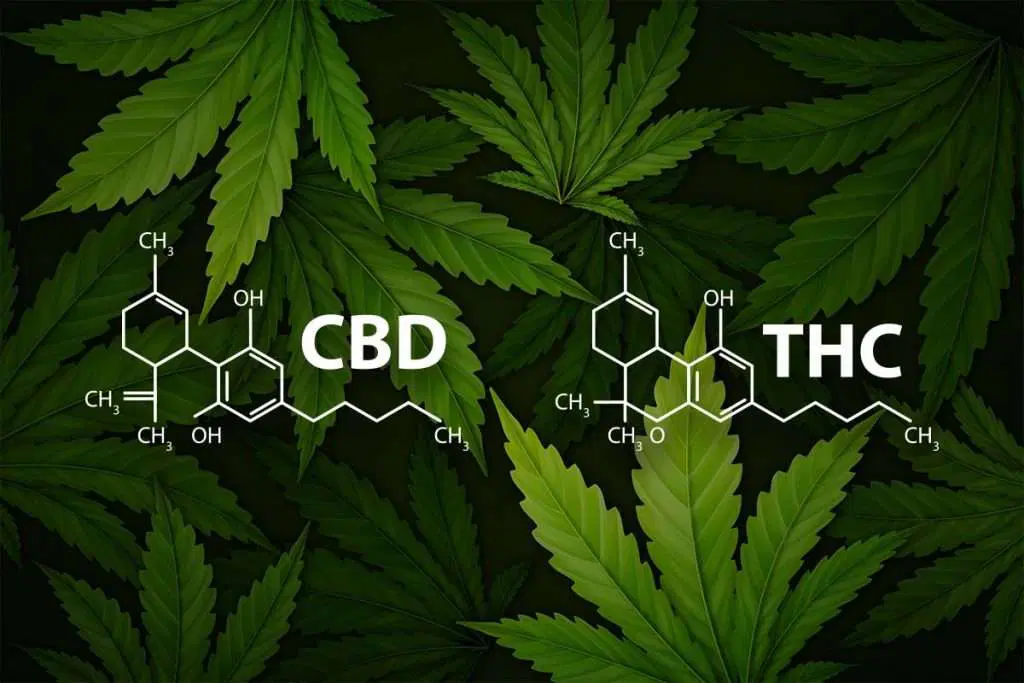
What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant, but they are also naturally produced by our bodies. They interact with the endocannabinoid system, a network of receptors spread throughout various parts of the body, to regulate functions such as sleep, pain, and mood.
The two most well-known cannabinoids are THC, which has psychoactive effects, and CBD, known for its relaxing and anti-inflammatory properties.
Cannabinoid-Based Therapies
Medical cannabis is used in various therapeutic fields. Let’s take a brief look at the scientific overviews published that confirm the effectiveness of cannabinoids in treating the aforementioned conditions.
Chronic Pain Treatment
Effectiveness: Medical cannabis has proven effective in reducing chronic pain.
Mechanism: The endocannabinoids in cannabis interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors, modulating pain perception.
Study: According to a study conducted by Dr. Kevin P. Hill, published in the Journal of Pain Research in 2017, cannabis treatment resulted in a significant reduction in chronic pain in patients compared to a placebo.
Muscle Spasticity in Multiple Sclerosis
Effectiveness: Medical cannabis can reduce muscle spasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis.
Mechanism: Cannabinoids affect the receptors of the endocannabinoid system, regulating muscle tone.
Study: A clinical study conducted by Dr. Olaf Stuve, published in the European Journal of Neurology in 2019, demonstrated that the use of cannabis resulted in a significant reduction in spasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis.
Symptoms of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with Chemotherapy
Effectiveness: Medical cannabis is effective in controlling chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.
Mechanism: Cannabinoids act on CB1 receptors in the brain, which regulate vomiting.
Study: According to a systematic review conducted by Dr. Sachin Patel, published in JAMA in 2020, cannabinoids are more effective than traditional treatments for chemotherapy-associated nausea and vomiting.
Drug-Resistant Epileptic Seizures
Effectiveness: Medical cannabis, particularly CBD, has shown promising results in reducing the frequency of epileptic seizures in patients resistant to medications.
Mechanism: CBD exhibits anticonvulsant effects by modulating endocannabinoid system receptors and other neurological pathways.
Study: A study conducted by Dr. Orrin Devinsky et al., published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2017, reported a significant reduction in seizures in patients with Dravet syndrome treated with CBD compared to a placebo.
Who Can Prescribe Medical Cannabis?
Medical Cannabis, like all medications, can be prescribed by any doctor who, based on their professional judgment and expertise, considers it the most appropriate therapy for the patient.
Therapies involving the use of cannabis extracts are adopted when traditional medications prove ineffective or cause intolerable side effects for the patient.
Cannabis is a phytocomplex whose therapeutic power does not come from a single active ingredient but from the synergistic effect of all its molecules.
This is why consulting an informed doctor who can recommend the best therapy based on the specific clinical case is essential.
What is meant by Phytocomplex?
The term “phytocomplex” refers to the set of active compounds present in a plant that work synergistically to enhance therapeutic benefits. In other words, it is not a single active ingredient that produces effects, but the interaction of all the molecules present, such as vitamins, minerals, essential oils, and other compounds.
This combined effect makes the phytocomplex more effective and balanced compared to isolated components. It is a concept often used in phytotherapy to describe the comprehensive benefits of medicinal plants.
How Do Cannabinoids Work?
The cannabinoids in cannabis interact with the endocannabinoid system through CB1 and CB2 receptors, which are distributed at specific points in the body. These receptors represent the areas where cannabinoids act, producing their therapeutic effects.
Medical cannabis is cultivated following precise standards, adhering to the principles of international guidelines for good agricultural and manufacturing practices to ensure the safety and efficacy of the medication.
Specifically, we are referring to the GACP and GMP certifications.
The GACP certification pertains to “Good Agricultural and Collection Practices for Medicinal Plants,” covering all regulatory references and general technical guidelines necessary to obtain high-quality medicinal plant materials for sustainable drug production.
The GMP certification establishes the set of rules and procedures that ensure the appropriate quality of manufactured products.
AIFA (Italian Medicines Agency) is the authority responsible in Italy for coordinating and managing inspections to verify compliance with the manufacturing and importation standards for active substances.
Do You Know the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is a cellular communication system made up of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), endocannabinoids (anandamide and 2-AG), and enzymes. It is involved in regulating various physiological functions, such as pain, mood, appetite, and the immune system.
Roles of Cannabinoid Receptors:
- CB1 receptors interact with neurotransmitters, aiming to protect the central nervous system from overstimulation.
- CB2 receptors regulate the activity of the immune system.
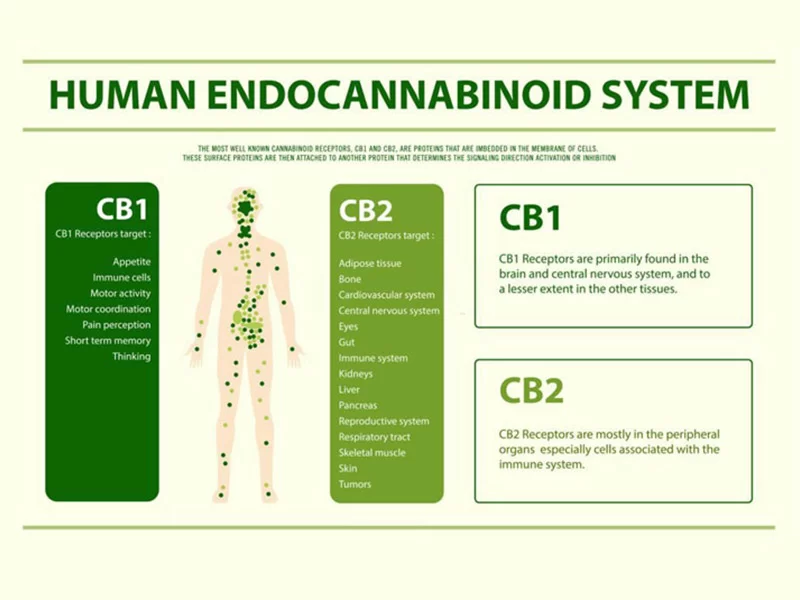
CB1 receptors are found in human cells such as muscles, lungs, reproductive organs, the liver, and the cardiovascular system.
CB2 receptors, on the other hand, are located peripherally in cells of bones, the spleen, the colon, the pancreas, and the immune system.
Endocannabinoids:
Endocannabinoids are molecules that monitor external conditions and activate receptors to transmit signals to cells, enabling a response to be triggered.
The first two molecules identified in the system were anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
Once they have performed their function, endocannabinoids are broken down by enzymes responsible for degrading these molecules. This process prevents an accumulation of endocannabinoids within the body.
Request a Specialized Consultation!
- Consult with a specialized doctor to understand your situation
- Personalized appointment scheduling on the days and times you prefer
- Receive the video call link in your email inbox
- Video call from anywhere: all you need is an internet connection.